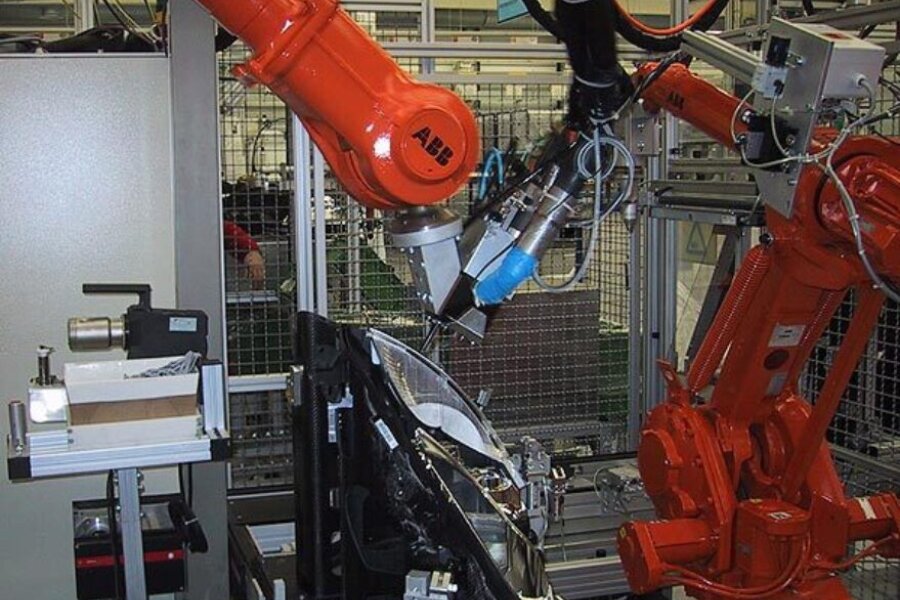
Automotive Interior
Roof linings, cockpit or instrument panel, dashboard, centre console, seats and headrests, door panels as well as door mirrors or parapets, armrests, A- / B- / C-pillars, trunk equipment are finished with fabrics, foils, leather or other materials. The adhesive is applied to a wide variety of materials with balti hotmelt systems in dot or caterpillar form, usually by means of automatic robot application, or flat by spraying, slot nozzle or roller technology prior to laminating, laminating, folding, joining or pressing.
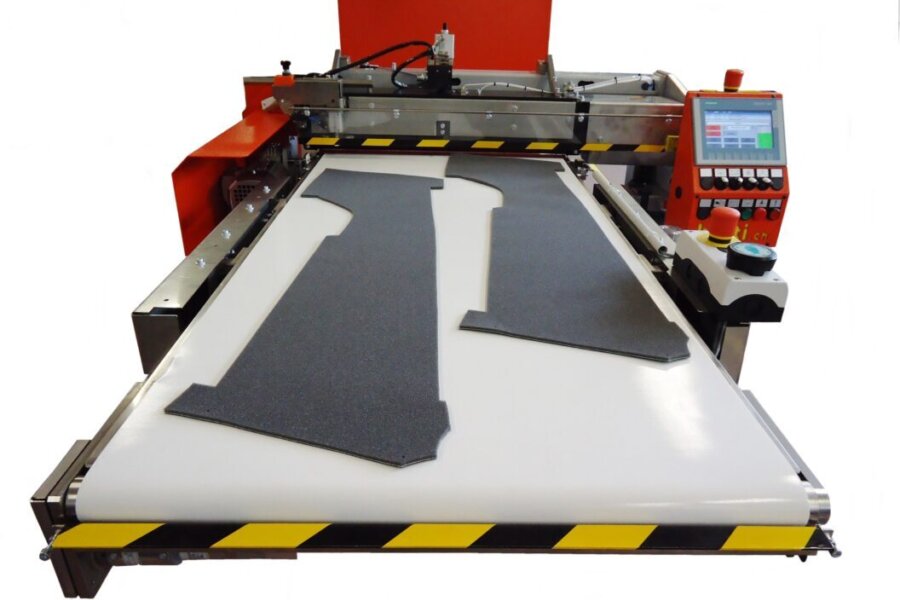
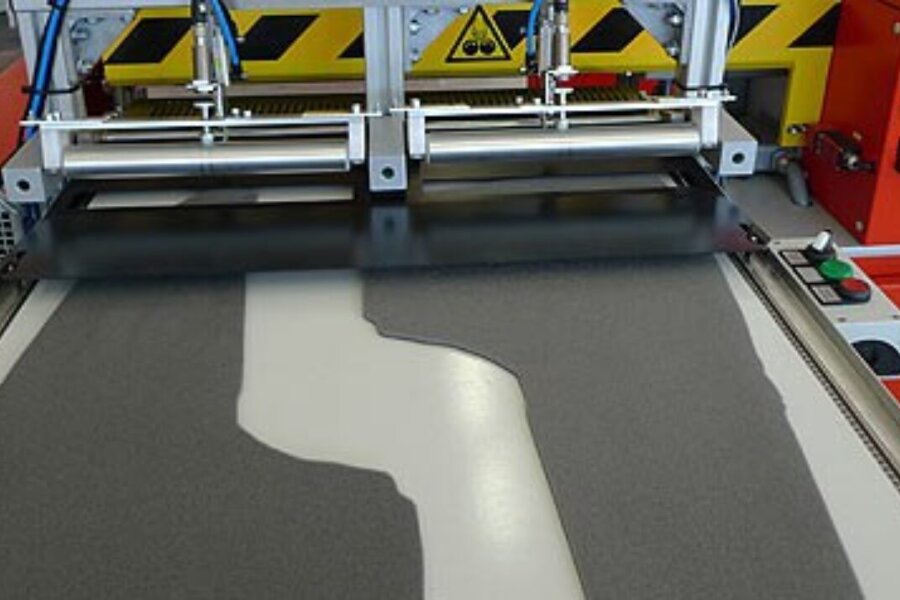
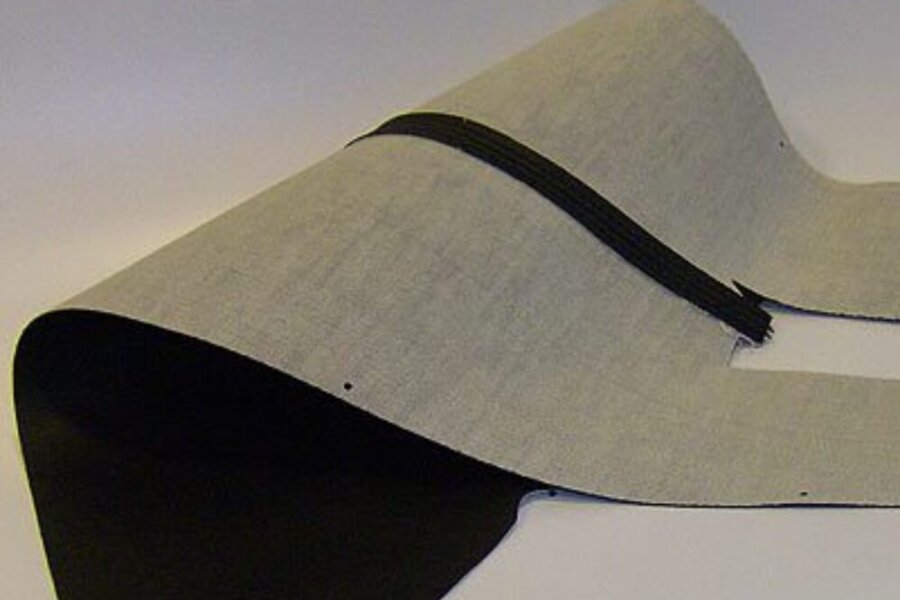



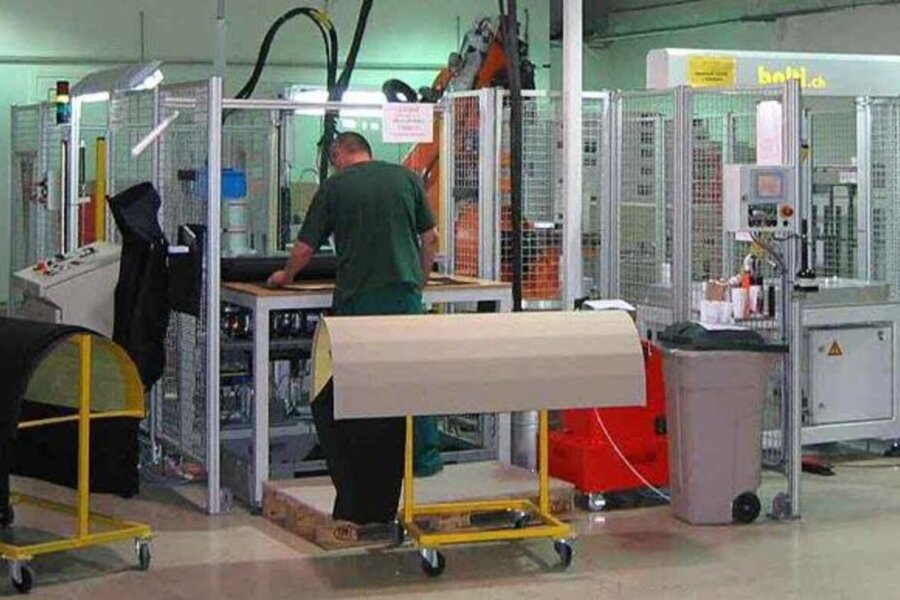
Coating of sheets prior to lamination
Cut-to-size fabrics, foils, foam foil composites or leather are first coated with a roller applicator and then reactivated on laminating machines and pressed with the carrier part.

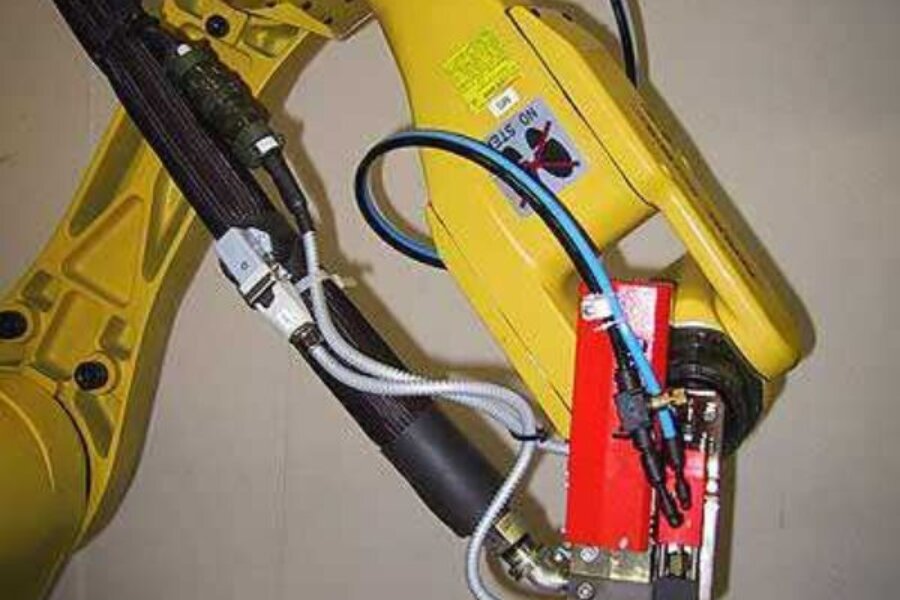
Bead application prior to edge folding
An adhesive valve or precision dosing pump valve is used by a robot to apply adhesive to the protruding and already laminated material before folding.
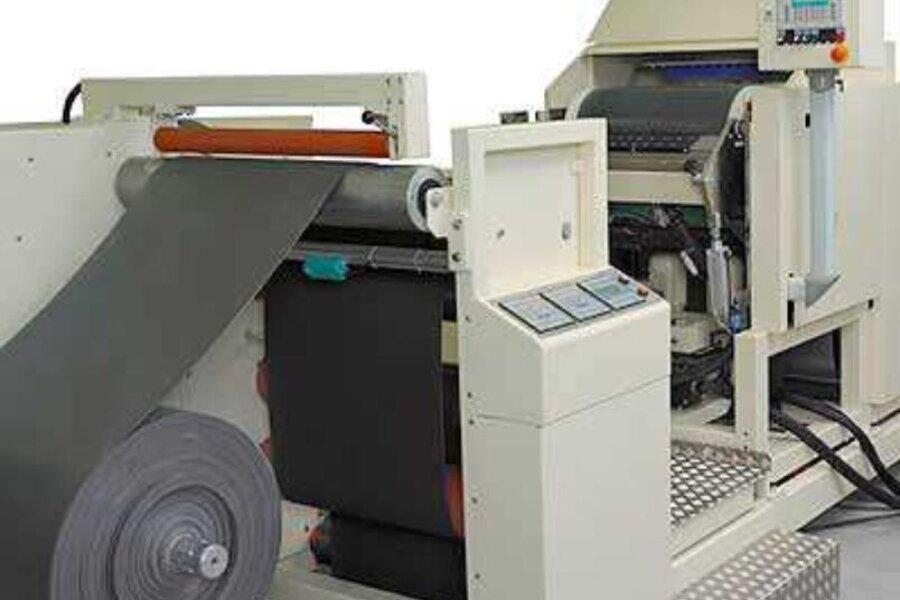

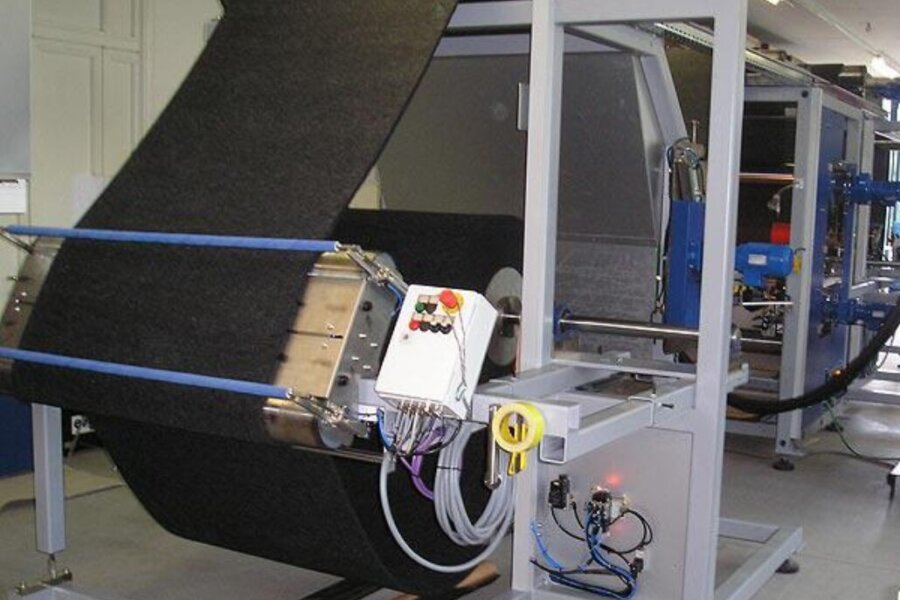
Coating fabric/foil from roll to roll
Often, endless fabric, film, foam film, etc. is first coated with reactive adhesive on a coating stand before being vacuum or press laminated on separate systems. Directly linking the systems can sometimes be useful in order to obtain compact, self-contained systems.
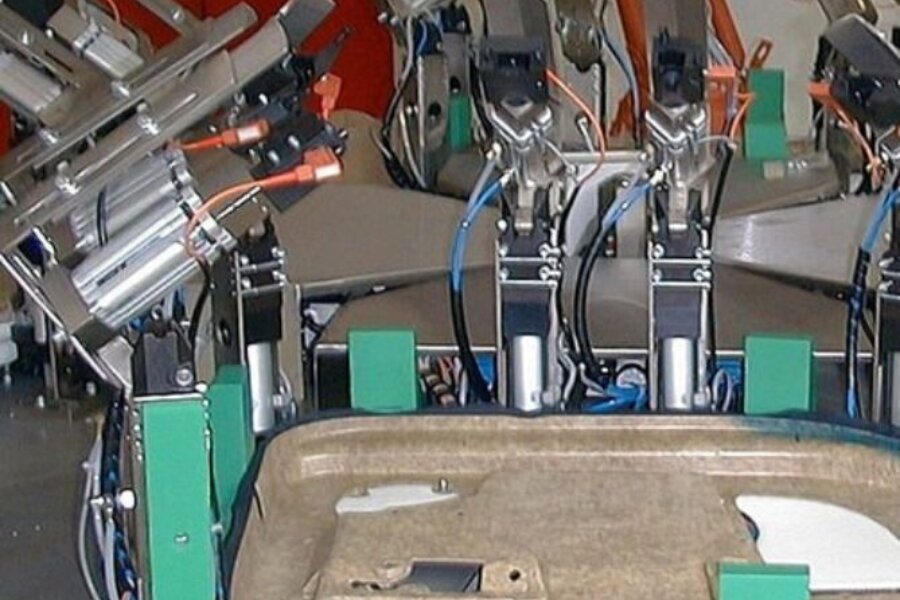
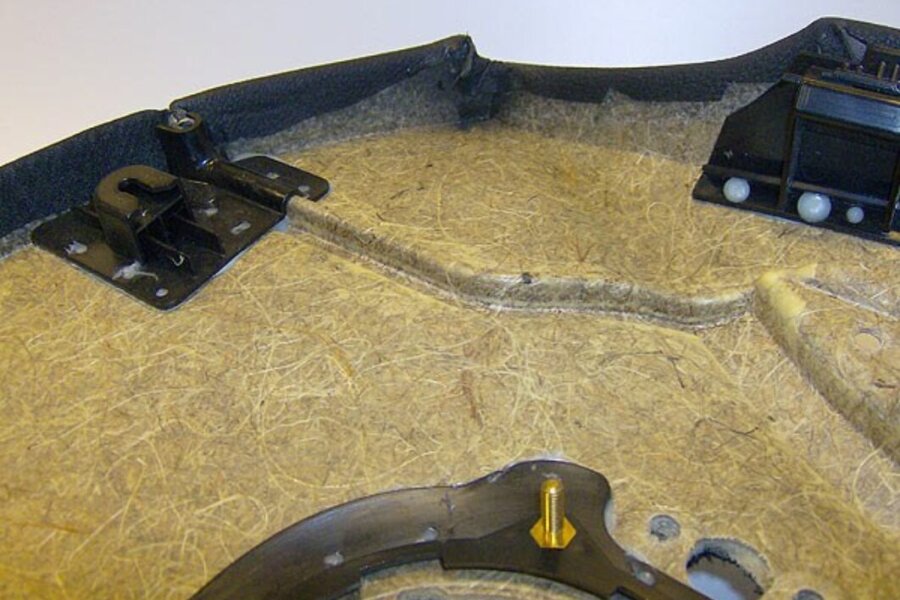


Bead application for glueing of retainer / ledge
Depending on the number of pieces, bead and spray application is applied manually or by robot on retainers or intended gluing points on the carrier (e.g. environmentally friendly fibre composite carrier parts) and then joined together in the same way. balti has already supplied complete systems in this area, e.g. with rotary indexing table or partially monitored manual application. The latter e.g. with PUR system, multiple workstation, automatic switch-off of unused application stations, time help/alarms for operators glue application, joining time etc.
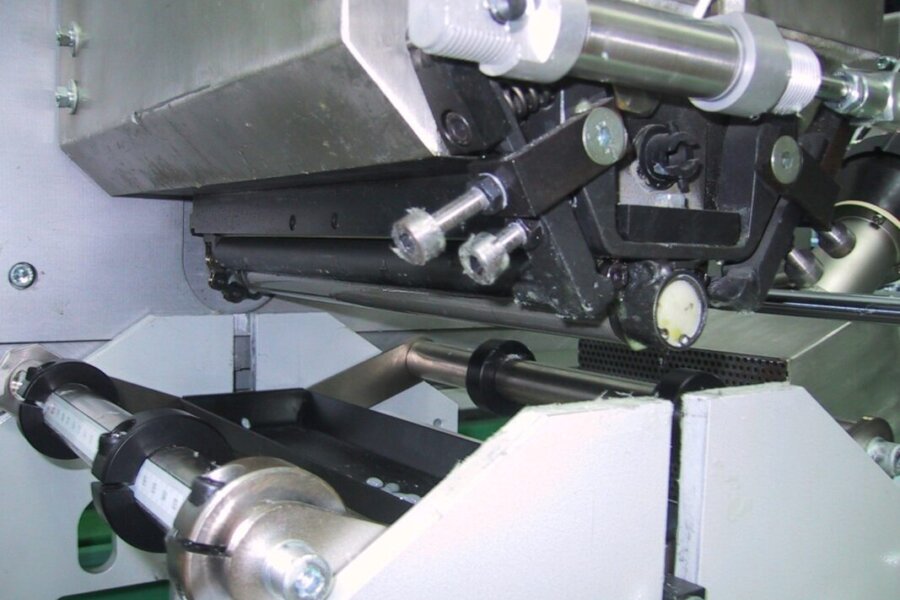
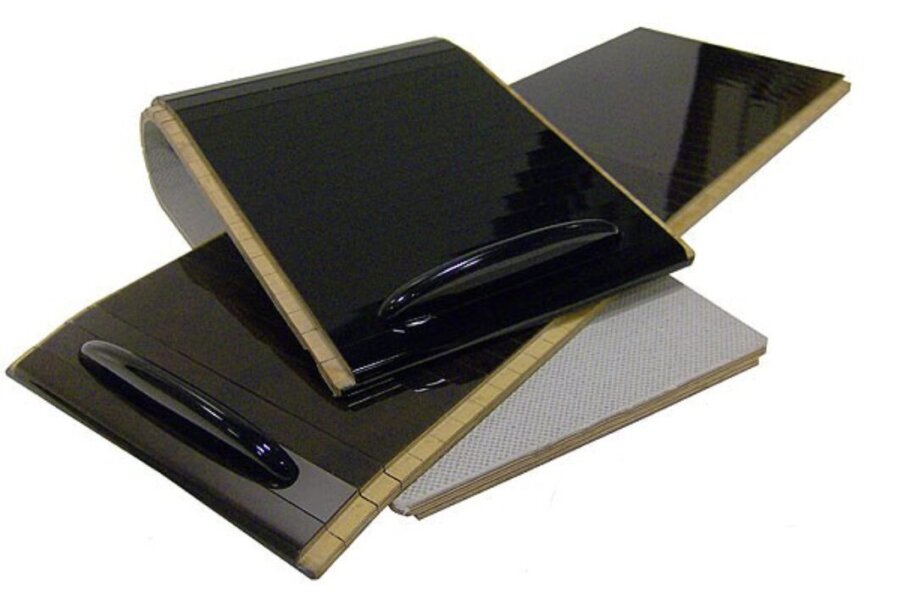
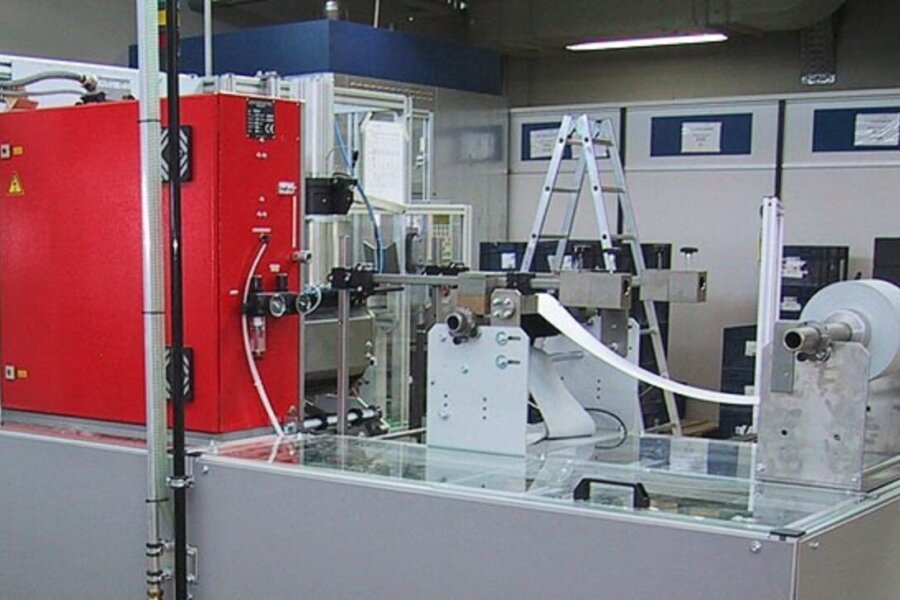



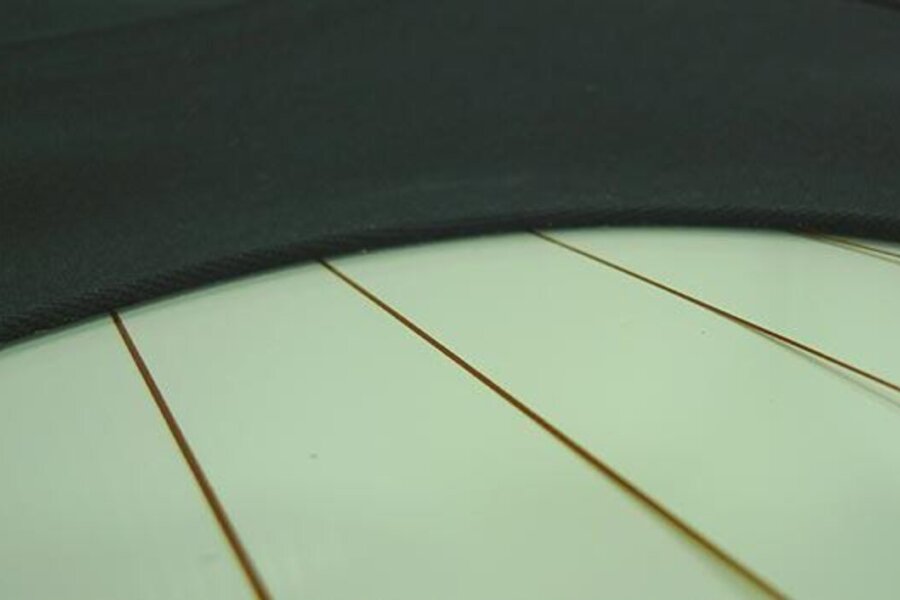
Laminating roller blinds / attaching labels
Compartments and storage areas, as well as their covers/lids, can be glued with hot melt adhesive. Whether it's just a handle, a label attached to a knob or ashtray with adhesive, or slats held together with a fabric connection and laminated with a hinge function to form roller blinds, balti can also offer complete concepts here.